The Applications of Fintech in the Insurance Industry
Insurance has existed for thousands of years. The earliest known reference is the Code of Hammurabi – a code of law from ancient Babylon dating back to at least the 18th century BCE that outlines the obligations of debtors and creditors.1
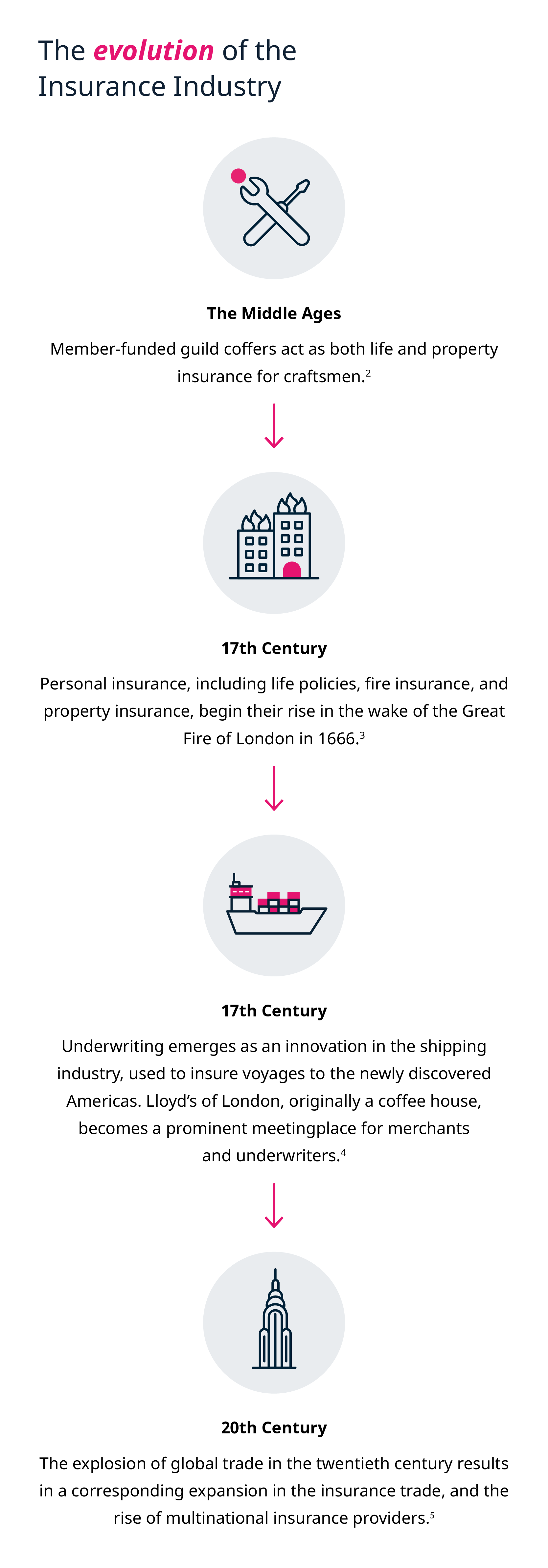
The insurance industry is now undergoing a shift, as fintech makes its impact felt at every level of global business. Insurers are grappling with ways to stay current and adapt to new, disruptive technology.
Fintech in the insurance industry
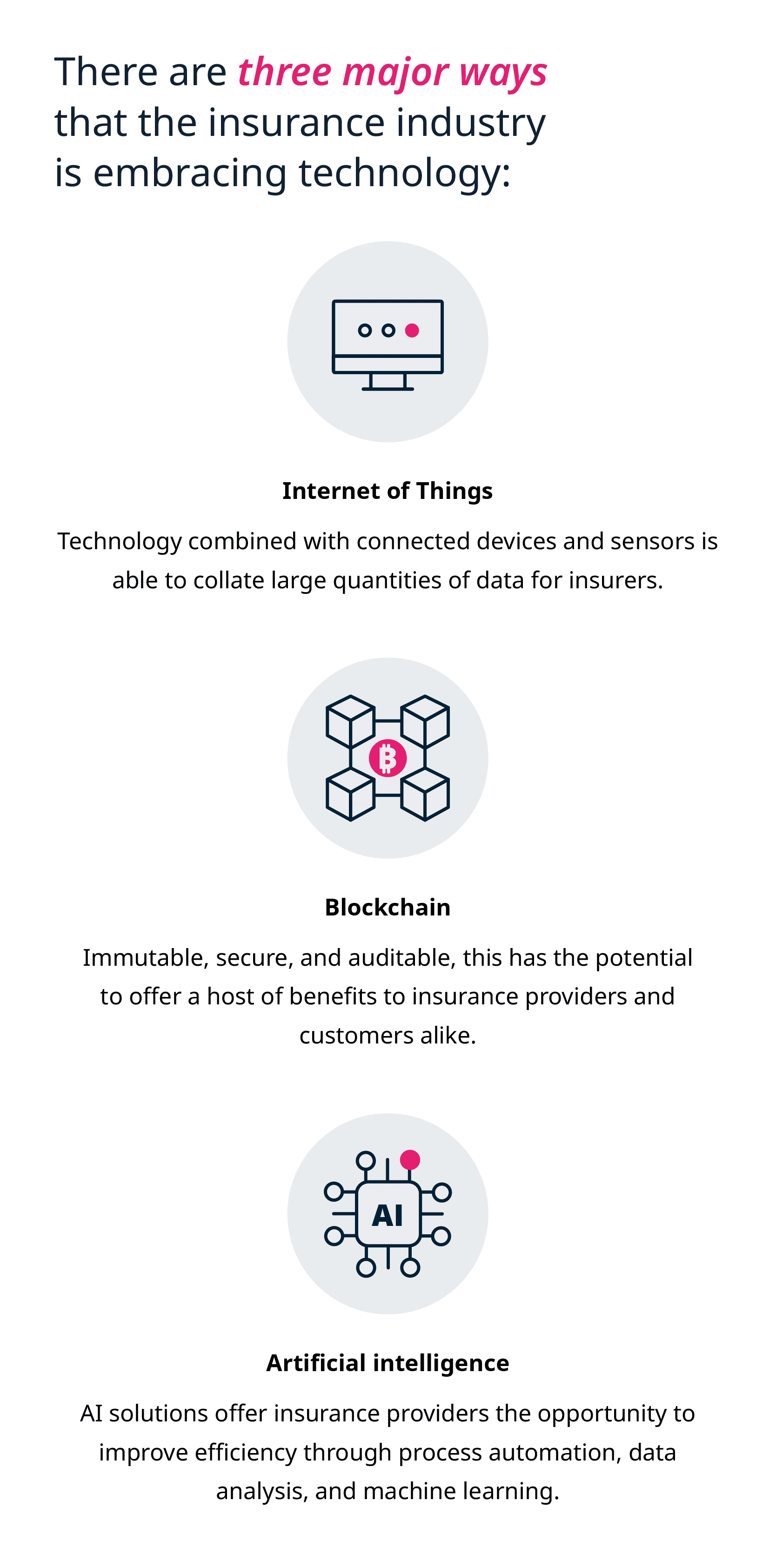
Internet of Things
![]()
Risk determination: Using data insights from sensors that are now commonplace in cars, insurers are able to determine risk more accurately through driver behavior.6
![]()
Safety and active prevention: Monitoring software in cars and mobile phones can detect accidents and quickly dispatch emergency services.7 Sensors in home devices such as geysers detect leaks, avoiding expensive claims.8
![]()
Usage-based pricing: The use of sensors in different environments provides data that can enable more individual risk calculation, and thus more granular pricing models. Customers who use smart devices are able to offer a more complete risk profile, potentially lowering product costs.9

Blockchain
![]()
Security: The immutability of the blockchain ledger provides a high level of security that’s highly resistant to tampering by malicious parties.11
![]()
Fraud detection: Duplicate claims can easily be spotted on the blockchain.12
![]()
Transparency: One of blockchain’s key strengths is its transparency – anyone with access can view the information, knowing that the decentralized system has verified the data’s accuracy.13
![]()
Smart contracts: By automating contracts on the blockchain, insurers increase operational efficiency, while customers enjoy the benefits of a quicker resolution process.14

Artificial intelligence
![]()
Automation: Robotic process automation (RPA) systems allow insurers to automate formerly manual processes and reduce mistakes, particularly in activities involving data collection and entry.16
![]()
Fraud detection: If fed accurate, deep data at sufficient volumes, machine learning algorithms can help insurers more quickly and effectively identify potential fraud.17
![]()
Customer satisfaction: AI solutions offer a number of ways to improve customer satisfaction and retention. Chatbots can quickly process customer requests through websites or apps, while RPA can be used to process claims efficiently.18
![]()
Risk calculation: With connected devices and data collected from diverse sources including social media, AI systems can offer more accurate risk assessments.19

While the fundamentals of the insurance industry remain grounded in principles developed thousands of years ago, it is presently undergoing a significant evolution as new technologies enable faster, more efficient risk calculation and claims processing. The onus lies on insurers to identify the most relevant technology and how best to apply it to their operations.
Step beyond current FinTech disruption and prepare for future financial services priorities with Harvard VPAL’s FinTech course.
- 1 Beattie, A. (May, 2021). ‘The history of insurance’. Retrieved from Investopedia.
- 2 Beattie, A. (May, 2021). ‘The history of insurance’. Retrieved from Investopedia.
- 3 Greene, M. (Nd). ‘Insurance’. Retrieved from Britannica. Accessed December 14, 2021.
- 4 Beattie, A. (May, 2021). ‘The history of insurance’. Retrieved from Investopedia.
- 5 Greene, M. (Nd). ‘Insurance’. Retrieved from Britannica. Accessed December 14, 2021.
- 6 Sun, S., et al. (May, 2020). ‘Assessing driving risk using internet of vehicles data: An analysis based on generalized linear models’. Retrieved from MDPI.
- 7 Singh, J., et al. (Apr, 2021). ‘Vehicle accident detection system using Internet of Things (VADS -IoT)’. Retrieved from IEEE Xplore.
- 8 Cericola, R. (Jul, 2021). ‘The best smart water-leak detector’. Retrieved from The New York Times.
- 9 (Feb, 2020). ‘Usage-based vehicle insurance’. Retrieved from IoT For All.
- 10 EG, M. (Apr, 2021). ‘Top 10 weather intelligence companies in 2021’. Retrieved from Analytics Insight.
- 11 (Aug, 2021). ‘How blockchain is disrupting insurance’. Retrieved from CB Insights.
- 12 Tropea, J. (Apr, 2021). ‘Insurance disruption: How blockchain is transforming the industry’. Retrieved from Bankrate.
- 13 (Aug, 2021). ‘How blockchain is disrupting insurance’. Retrieved from CB Insights.
- 14 (2021). ‘Discussion paper on blockchain and smart contracts in insurance’. Retrieved from European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority.
- 15 Copigneaux, B., et al. (2020). ‘Blockchain for supply chains and international trade’. Retrieved from European Parliamentary Research Service.
- 16 Williams, P. (Jun, 2021). ‘The case for robotic process automation (RPA) in insurance’. Retrieved from IBM.
- 17 Hulett, J. (Jul, 2020). ‘Artificial intelligence in claims fraud: How AI is automating suspicious behavior detection’. Retrieved from Verisk.
- 18 Williams, P. (Jun, 2021). ‘The case for robotic process automation (RPA) in insurance’. Retrieved from IBM.
- 19 Eling, M., et al. (Feb, 2021). ‘The impact of artificial intelligence along the insurance value chain and on the insurability of risks’. Retrieved from Springer.
- 20 (Nd). ‘AI and automation improve insurance claims process’. Retrieved from Cognizant. Accessed December 16, 2021.