A Guide to Blockchain Technology for Business
When Bitcoin, a “purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash”, was released in 2008, blockchain (the technology that runs Bitcoin) made its public debut.1 The brainchild of a person or group known by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, its expansive technological capabilities were then somewhat unknown. Fast forward 12 years to 2020, there’s now a growing recognition that blockchain can serve as a pragmatic solution to various business problems across industries. Identified as a general-purpose technology (GPT), blockchain is similar in scope to the disruptive power of the internet, the steam engine, and electricity. Even business leaders wary of tech-based solutions and global ‘hype’ have come to realise the larger, transformational importance of this digital technology.2
In order to revolutionise business and redefine companies and economies utilising blockchain technology, it’s necessary to have a foundational understanding of its capabilities and applications.
What is blockchain, and how can we apply it?
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger capable of recording and verifying a high volume of digital transactions. New information can be added to the record, but previous information, stored in blocks, cannot be edited, adjusted, or changed.3 The ledger can be used to track not only financial transactions, but any digital asset transaction, making it possible to share contracts, information, cryptocurrencies, and more.4 Additionally, blockchain is a decentralised system, which means the information in the blockchain ledger isn’t maintained by a single controlling entity or intermediary, but hosted across a shared network of devices, making the system almost tamper-proof.5
With blockchain, we have the potential to live in a world where contracts are embedded in digital code and stored in transparent, shared databases where they’re protected from deletion, tampering, and revision.6 By allowing digital information to be distributed with each copy simultaneously updated, blockchain technology has created the backbone for a new type of internet.
The disruptive potential of blockchain
The last few decades brought us the internet of information. We’re now witnessing the rise of the internet of value. Where the first era was sparked by a convergence of computing and communications technologies, this second era is powered by a clever combination of cryptography, mathematics, software engineering, and behavioural economics.7 According to Don Tapscott, a leading analyst of innovation and the impact of technology, “Blockchain technology will have a dramatic impact on business and society by providing a secure, direct way of exchanging money, intellectual property and other rights and assets without the involvement of traditional intermediaries like banks, utility companies and governments.”8
Technological innovation can impact more than just our daily lives. It can disrupt entire industries and change the way enterprises do business. As new technologies develop, affected industries are forced to adapt or be left behind.9
A 2019 Deloitte survey reveals a continued strong investment in blockchain, with those willing to invest up to $5 million or more in new blockchain initiatives over the next 12 months. Among the finance and banking sectors, blockchain has the potential to lower overheads and labour costs.10 Initially, financial services and, specifically, the financial technology (fintech) sector were leading in blockchain development, while other industries were acting with caution. Leaders were questioning whether the return on investment justifies the cost and effort of implementing blockchain solutions. Today, fintech remains a blockchain leader, but more organisations in multiple sectors – such as media, telecommunications, healthcare, and government – are expanding and diversifying their blockchain potential.11
You only have to consider the five underlying principles of blockchain technology to realise its potential to disrupt various processes across diverse industries. These include:12
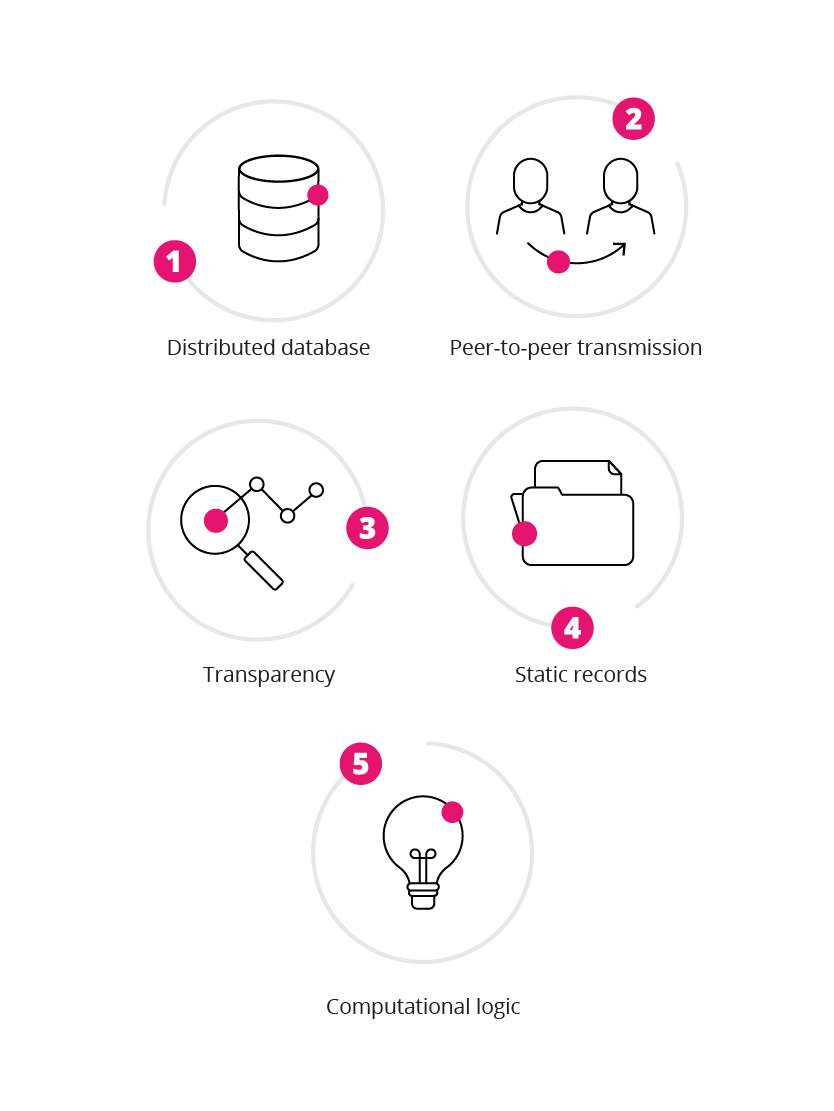
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionise the world economy. Its ability to facilitate collaboration and tracking of all kinds of transactions and interaction across various processes means it can be used across disciplines. Indeed, some blockchain proponents believe that the real potential of blockchain is only just being discovered.
How to apply blockchain to a business
Blockchain technology can be applied to any sector or industry that needs an accurate record of information. As blockchain becomes more accessible and popular, it’s starting to revolutionise a vast number of industries and business models on a global scale.13
In the early stages of blockchain applications, a World Economic Forum survey suggested that 10% of global GDP will be stored on blockchain by 2027.14 Multiple governments have published reports on the potential implications of blockchain, and the past two years alone have seen more than half a million new publications on blockchain, not to mention more than 3.7 million Google search results.15 Its potential to transform industries, ensuring transparency and efficiency, has resulted in a global hype. In some cases, the hype is warranted; in others, valueless.
To determine whether companies should invest in blockchain, it’s necessary to focus on real-world use cases and their market position.16 While complementary technology and supporting platforms around the blockchain ecosystem are sure to evolve, some industries benefit more from it than others.
The impact of blockchain on supply chain management
A century of change has shown us that supply chains – the links to creating and distributing goods – are regularly disrupted by innovation. In today’s world, companies need to be agile, flexible, and responsive, by driving continuous innovation throughout their business supply chain, in order to remain competitive and relevant.17
Managing today’s supply chains is extremely complex. Depending on the product, the supply chain can cover hundreds of stages across multiple geographical locations, include a multitude of invoices and payments, have several individuals and entities involved, and extend over months.18 Due to this complexity, blockchain is an attractive means to transform the supply chain and logistics industry.19
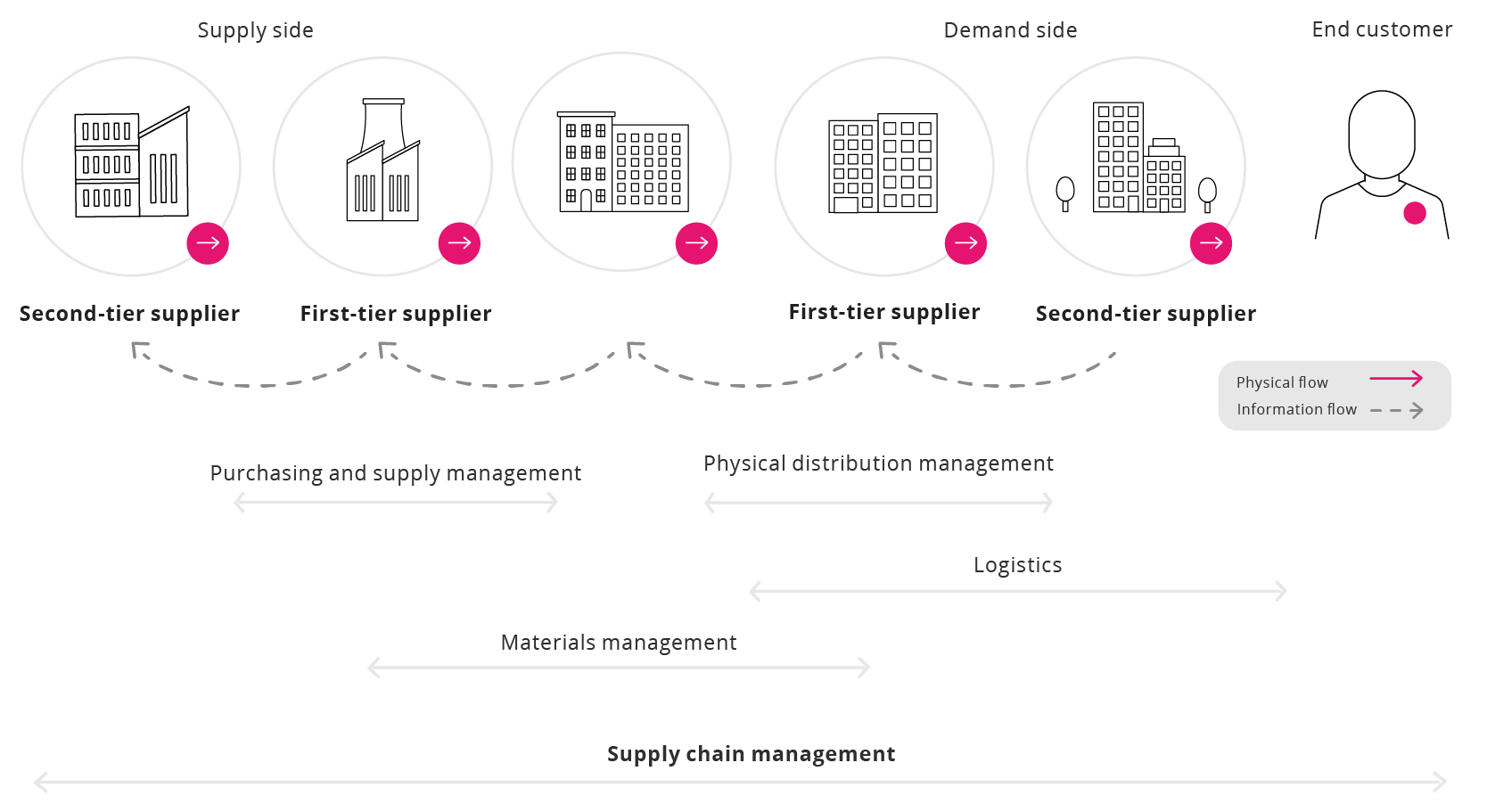
The transparency, efficiency, and scalability of blockchain is replicated within/transferred to supply chains, and can positively impact various business divisions, from warehousing to payment to delivery.20 Since blockchains allow for the transfer of funds from anywhere in the world, without the use of a traditional bank, a globalised supply chain is convenient. It can provide:
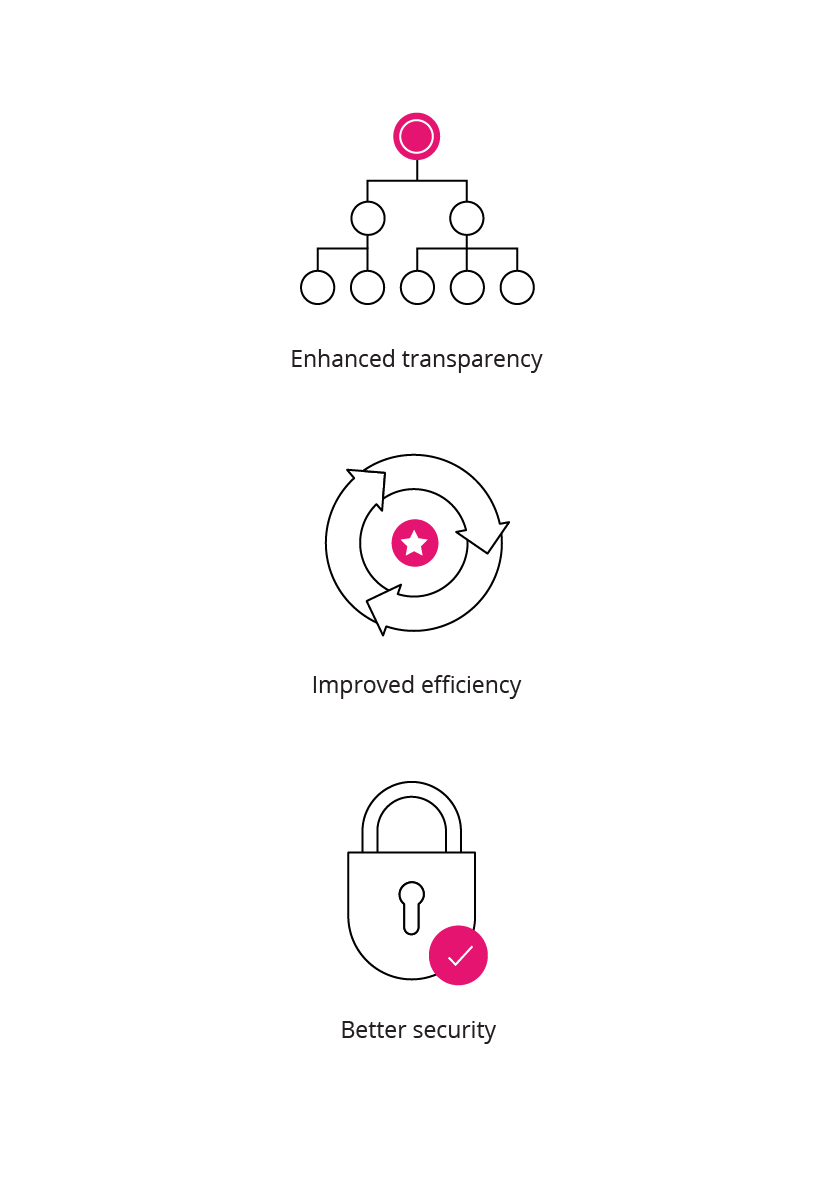
The potential of blockchain in a struggling economy
The records of contracts and transactions are among the defining structures in our economic, legal, and political systems. However, the critical tools formed to manage these notations haven’t kept up with the economy’s digital transformation.21 Blockchain has the potential to solve this problem.
Stay Competent, Confident, and Informed
Sign up to our monthly newsletter to receive the latest course information, expertise from renowned thought leaders, and a summary of our most recent blog articles.
As a foundational technology, blockchain has the potential to create a new platform for our economic and social systems. Before the technology was developed, there was no way to secure and validate ownership in a digital asset, or verify a transaction in a trustless, public way. With blockchain, contracts are now embedded in digital code and stored in transparent and protected databases. From finance to customs and certification processes, transportation and logistics, insurance, distribution, intellectual property, and government procurement, the applications of blockchain are immense.22 As a result, our traditional association and understanding of intermediaries in these sectors – like lawyers, brokers, and bankers – is at risk of disruption.
Blockchain enables innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the internet of things (IoT) so that more people can exchange digital information and ultimately create a new form of shared governance.23
Prepare for a blockchain future
Although blockchain technology is set to be a significant player in the future digital economy, many business leaders remain unsure of what it means for their companies going forward. Blockchain skills have become one of the most sought-after proficiencies in the world, with the demand increasing by almost 2,000% between 2017 and 2020.24 David Furlonger, Distinguished Research VP at Gartner, noted how, “Sixty percent of CIOs in the Gartner 2019 CIO Agenda Survey said that they expected some level of adoption of blockchain technologies in the next three years.”25
There’s no denying that, with each new blockchain use case, comes a heightened excitement for its potential. Blockchain today might feel like the internet in 1993, but a decade from now, you’ll wonder how society ever functioned without it.
- 1 Marr, B. (Feb, 2018). ‘A Very Brief History of Blockchain Technology Everyone Should Read’. Retrieved from Forbes.
- 2 Budman, M, Hurley, B, et al. (2019). ‘Deloitte’s 2019 Global Blockchain Survey’. Retrieved from Deloitte.
- 3 Iinuma, A. (Apr, 2018). ‘What Is Blockchain And What Can Businesses Benefit From It?’ Retrieved from Forbes.
- 4 Fortney, L. (Jun, 2019). ‘Blockchain Explained’. Retrieved from Investopedia.
- 5 Fortney, L. (Jun, 2019). ‘Blockchain Explained’. Retrieved from Investopedia.
- 6 Iansiti, M & Lakhani, K. R. (Feb, 2017). ‘The Truth About Blockchain’. Retrieved from Harvard Business Review.
- 7 Techutzpah. (Mar, 2018). ‘Blockchain Choking Hazard’. Retrieved from The IoT Magazine.
- 8 MacIver, K. (Jul, 2016). ‘From the internet of information to the internet of value’. Retrieved from I-CIO.
- 9 White, J. (Mar, 2018). ‘9 Industries That Will Soon Be Disrupted By Blockchain’. Retrieved from Inc.
- 10 Pratap, M. (Jul, 2018). ‘How is Blockchain Revolutionizing Banking and Financial Markets’. Retrieved from Hackernoon.
- 11 Budman, M., Hurley, B., et al. (2019). ‘Deloitte’s 2019 Global Blockchain Survey’. Retrieved from Deloitte.
- 12 (Dec, 2018). ‘The potential disruptive power of blockchain technology’. Retrieved from GetSmarter.
- 13 (Mar, 2018). ‘Revolutionise Your Business Strategy With An Investment In Blockchain Technology’. Retrieved from GetSmarter.
- 14 (Sep, 2015). ‘Deep shift: Technology Tipping Points and Societal Impact’. Retrieved from the World Economic Forum.
- 15 Carson, B., Romanelli, G., et al. (Jun, 2018). ‘Blockchain beyond the hype: What is the strategic business value?’. Retrieved from McKinsey.
- 16 Carson, B., Romanelli, G., et al. (Jun, 2018). ‘Blockchain beyond the hype: What is the strategic business value?’. Retrieved from McKinsey.
- 17 (Jan, 2019). ‘How Blockchain will Radically Improve the Supply Chain’. Retrieved from GetSmarter.
- 18 Marr, B. (Mar, 2018). ‘How blockchain will transform the supply chain and logistics industry’. Retrieved from Forbes.
- 19 Marr, B. (Mar, 2018). ‘How blockchain will transform the supply chain and logistics industry’. Retrieved from Forbes.
- 20 Marr, B. (Mar, 2018). ‘How blockchain will transform the supply chain and logistics industry’. Retrieved from Forbes.
- 21 Iansiti, M. & Lakhani, K. R. (Feb, 2017). ‘The Truth About Blockchain’. Retrieved from Harvard Business Review.
- 22 G, Emmanuelle. (2018). ‘Can Blockchain revolutionize international trade?’ Retrieved from IBM.
- 23 Likens, S. (Nd). ‘The Essential Eight: Your guide to the emerging technologies revolutionizing business now’. Retrieved from PWC.
- 24 Schlapkohl, K. (Apr, 2020). ‘Blockchain explained: The future of blockchain’. Retrieved from IBM.
- 25 Rimol, M. (Sep, 2019). ‘Gartner 2019 Hype Cycle for Blockchain Business Shows Blockchain Will Have a Transformational Impact Across Industries in Five to 10 Years’. Retrieved from Gartner.